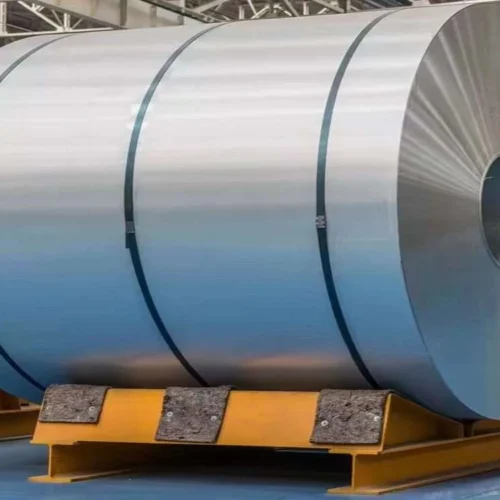
Product Description
Hot rolling divides into three types based on material and performance:
-
Ordinary carbon structural steel
-
Low alloy steel
-
Alloy steel
It can be divided based on different uses, including:
-
Steel for cold forming
-
Structural steel
-
Automotive structural steel
-
Corrosion-resistant structural steel
-
Mechanical structural steel
-
Steel for welding gas cylinders and pressure vessels
-
Steel for pipelines
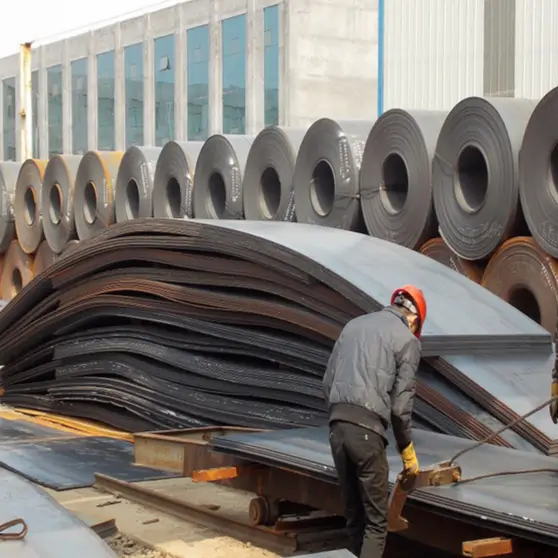
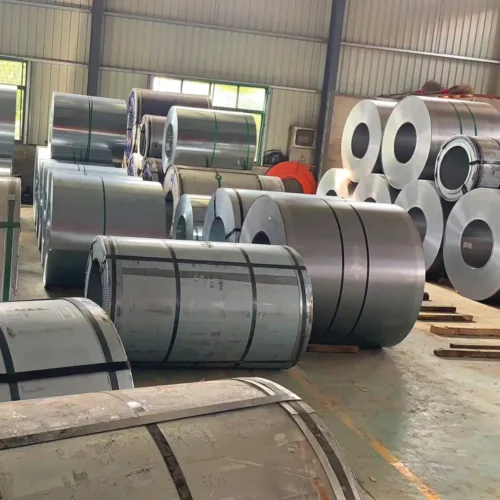
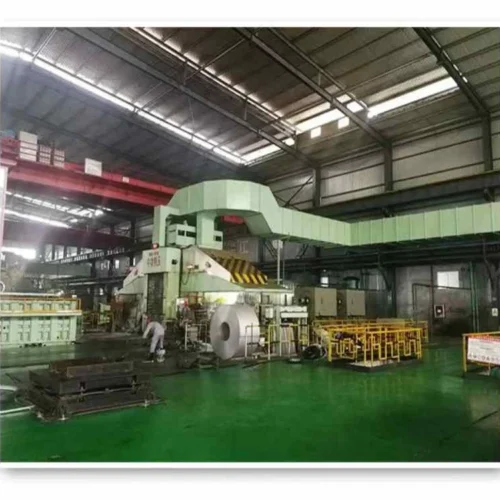
Hot-rolled coil starts with a continuous casting or blooming slab. First, it gets heated in a walking furnace. Then, high-pressure water descalers clean it. Finally, it goes into the rough rolling mill. Controlled rolling, laminar cooling, and coiling after rolling make straight hair coils. Coil Inner diameter is 760mm, Uses for ships, cars, bridges, HRB>90. The straight hair coils are usually tongue-shaped or fish-tail-shaped. They often lack thickness and width accuracy. The edges can have defects like wavy, hemmed, or tower shapes. Its coil weight is heavy. (The general pipe industry likes to use).
| Commodity: | Carbon steel coil |
| Standard: | DIN GB JIS BA AISI ASTM EN GOST ETC. |
| Mechnical: | Commercial / Drawing / Deep Drawing /Extra Deep Drawing/Structural quality |
| Surface treatment: | Chromated and oiled, and ant-ifinger |
| Hardness: | Softy, half hard ,hard quality |
| Grade: | DC01 |
| ST14,ST15,ST16,DC01,DC03,DC04,DC05,DC06,etc. | |
| Thickness: | 0.12-12.0mm |
| Width: | 600-1500mm |
| Coil weight: | 3-34MT/Coil or as your request |
| MOQ: | 5MT |
| Packaging: | Export standard, seaworthy |
| ID: | 508mm or 610mm |
| Trade Term: | FOB, CFR, CIF, EXW ETC. |
| Transport Type: | Container, bulk and train |
Hot Rolled Steel Coil Usage
Hot-rolled coils start as slabs, mostly from continuous casting. After heating, they become strip steel through rough and finishing rolling units. The hot-rolled coil exits the last finishing mill. It cools to the set temperature using laminar flow, then is rolled into a steel coil by the coiler.
The cooled steel coil passes through different processes according to the different needs of users. The finishing line processes steel into several products. These include steel plates, flat coils, and slitting steel strips. The steps involve leveling, straightening, cross-cutting, slitting, inspection, weighing, packaging, and marking.
To put it simply, a billet is heated and rolled several times, then trimmed and straightened into a steel plate. This processing method is called hot rolling. Hot-rolled steel products are strong and tough. They’re also easy to process and weld. These qualities make them popular in many industries.
They are used in ships, cars, bridges, construction, machinery, and pressure vessels. New technologies are improving the control of hot-rolled steel sheets. They enhance dimensional accuracy, plate shape, and surface quality.
As new products keep emerging, the use of hot-rolled steel sheets and strips is growing. They are becoming increasingly important in the market. competitiveness.
Steel grades
1. SPHC—the abbreviation of the first S steel, P is the abbreviation of Plate, H is the abbreviation of Heat, and C is the abbreviation of Commercial. The whole indicates that hot-rolled steel plates and steel strips are generally used.
2. SPHD—Indicates hot-rolled steel sheets and strips for stamping.
3. SPHE—Indicates hot-rolled steel sheets and strips for deep drawing.
4. SPCC—Indicates cold-rolled carbon steel sheets and strips for general use. The third letter C is the abbreviation for Cold. When it is necessary to ensure the tensile test, add T at the end of the grade to represent SPCCT.
5. SPCD—indicates cold-rolled carbon steel sheets and strips for stamping.
6. SPCE—Indicates cold-rolled carbon steel sheet and strip for deep drawing. When it is necessary to ensure non-timeliness, add an N at the end of the grade to make it SPCEN.
Quenching and tempering codes for cold-rolled carbon steel sheets and strips are as follows:
-
A for annealed.
-
S for standard quenching and tempering.
-
8 for 1/8 hard
-
4 for 1/4 hard
-
2 for 1/2 hard
-
1 for hard
Surface processing code: D for dull finish rolling, B for bright finish rolling. SPCC-SD stands for standard quenched and tempered. It refers to a matte finish rolled general cold-rolled carbon sheet. Another example is SPCCT-SB. This stands for standard quenching and tempering, bright processing, and cold-rolled carbon sheets. These sheets need guaranteed mechanical properties.
7. The JIS mechanical structure steel grade is expressed as: S + carbon content + letter code (C, CK). The carbon content shows the median value multiplied by 100. Here, C stands for carbon, and K denotes carburizing steel. For example, carbon knot coil S20C has a carbon content of 0.18-0.23%.
Related products
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel
Carbon Steel